Here's What Really Matters in Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Since the inception of the whole idea of a decentralized currency, the world has been impacted in ways that can be described as both positively or negatively which basically depends on what part of the swinging pendulum of the volatile market you stand

Since the inception of the whole idea of a decentralized currency, the world has been impacted in ways that can be described as both positively or negatively which basically depends on what part of the swinging pendulum of the volatile market you stand in, Decentralized finance (DeFi) as explained by Investopedia is a financial system that eliminates intermediaries by allowing people, merchants, and businesses to conduct financial transactions through emerging technology. Through peer-to-peer financial networks, DeFi uses security protocols, blockchain technologies, connectivity, software, and hardware advancements. This whole concept enables transactions to be made with little or no interference by any regulatory body or third party.
How Does DeFi Work:
Decentralized finance uses the blockchain technology that cryptocurrencies use. A blockchain is a distributed and secured database or ledger. Applications called dApps are used to run transactions and run the blockchain.
On the blockchain, transactions are recorded in blocks and then verified by other users. If these verifiers approve a transaction, the block is closed and encrypted; another block is then formed that holds information about the previous block within it.
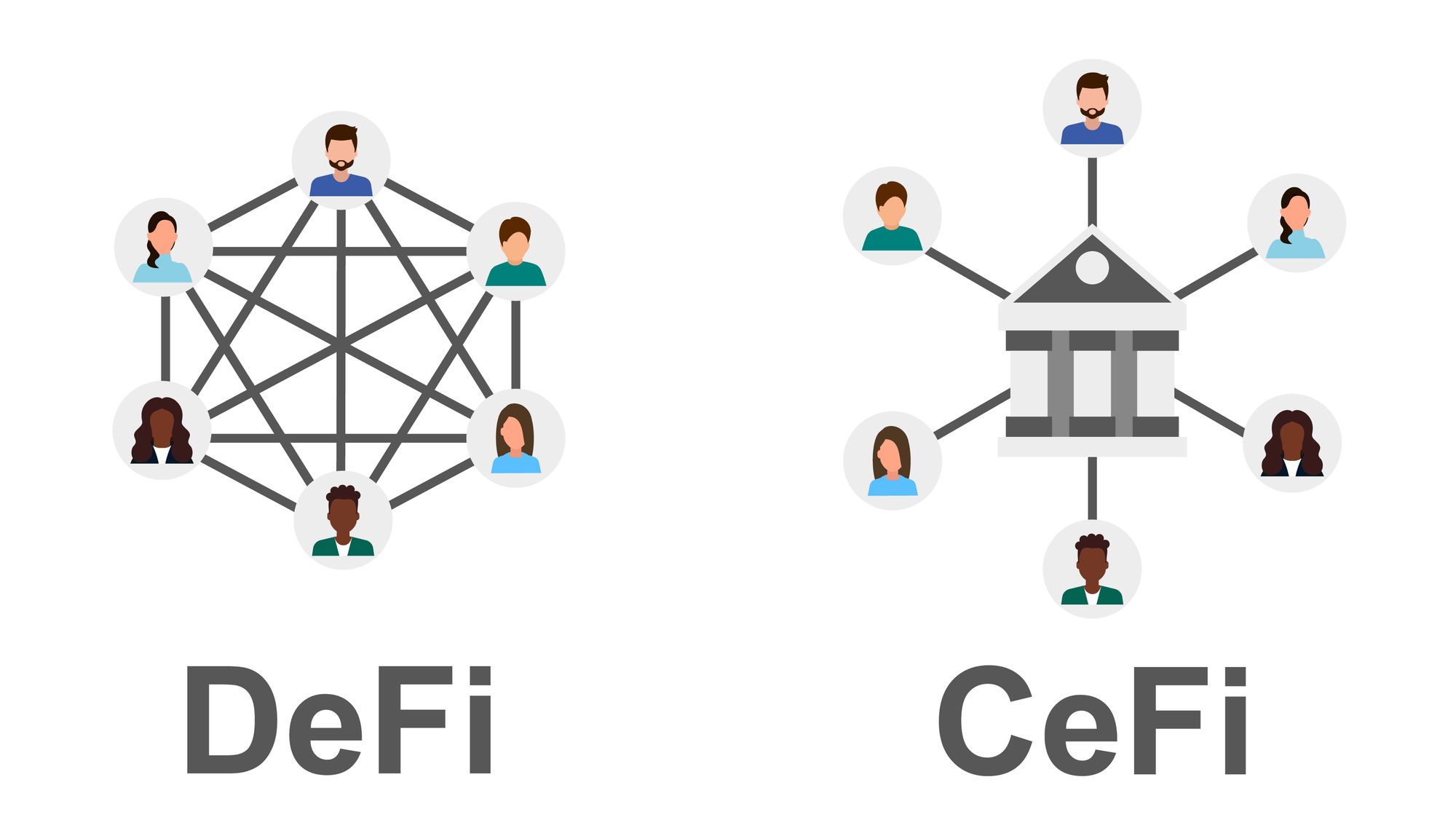
With DeFi, there is no central authority or body. Instead, authority is distributed in a decentralized approach that is considered to provide more power and control to users. In the DeFi model, all transactions for buying, selling, loans, and payments with cryptocurrency can occur without a central authority in a peer-to-peer (P2P) approach.
The custody of assets is a fundamental component of any financial model. In the DeFi approach, individual traders have control over the private cryptographic encryption keys, enabling cryptocurrency asset custody. Financial transactions within the DeFi model are allowed with a smart contract that is often supported on Ethereum-based blockchains.
Benefits Of DeFi:
- Decentralized. Because it's decentralized, DeFi is not subject to risks associated with CeFi (Centralized Finance), where the collapse of an exchange can lead to a complete collapse and loss of user funds and accounts.
- Programmed Response. As a decentralized model, there is no central authority to approve or enable a transaction. Instead, the model is permissionless as it adheres to the programmatic logic of smart contracts.
- Storage. In DeFi, users control assets, and storage of the cryptographic private key for cryptocurrency tokens, held by the user alone.
- Transparency. Running a transaction on the blockchain gives a clear-cut idea of what is going on so users would understand the programs and protocol to follow without any hidden code.
- Anonymity. While smart contracts can be transparent on the blockchain, there is no need for users to be identified and they can perform transactions anonymously. With DeFi, Know Your Client requirements, which are common with centralized and regulated models, do not specifically apply.

Limitations Of DeFi:
- Security. In recent years, DeFi platforms have increasingly been targeted by hackers. A Federal Bureau of investigation alert was issued in August 2022 warning that over $1 billion in assets had been stolen in just three months.
- Complexity. The perceived complexity of DeFi is likely the model's biggest challenge. DeFi works in a P2P model, with smart contracts and sophisticated algorithms that can be difficult to fully comprehend by some who aren't tech-savvy. That complexity can also lead to misconceptions about how an application works.
- Customer service. Without a central authority or service to ask for help, customer service with DeFi can often be a challenge.
- Volatility. Since there are no regulatory bodies to checkmate and limit the number of transactions, Defi stands the risk of building heavy volatility with its market momentum and surge.
Common Uses Of DeFi:
- Payments. DeFi can enable P2P payments without the need for a central authority.
- Lending. The ability to lend and borrow cryptocurrency assets is a common use case for DeFi.
- NFTs. Non-fungible tokens enable users to own tokens that can be traded.
- Stablecoins. An increasingly common use of DeFi is stablecoins. The purpose of a stablecoin is to help limit the volatility of cryptocurrency by pegging the value of a coin to another asset, commodity, or currency.
- Yield farming. For those using DeFi as an investment vehicle, yield farming enables individuals to gain interest income on cryptocurrency assets.
Notwithstanding DeFi has proven the feasibility of a world with a non-regulated financial system that can enable people to transact swiftly and hassle-free, although its flaws are still intrinsic we are hopeful that in years to come those minor glitches would have been corrected and the world will be able to embrace the decentralized financial system, furthermore, to transact on the blockchain network you will need Ethereum and stablecoins, to swap your cryptocurrencies quickly with a reasonable fee click on the link below.